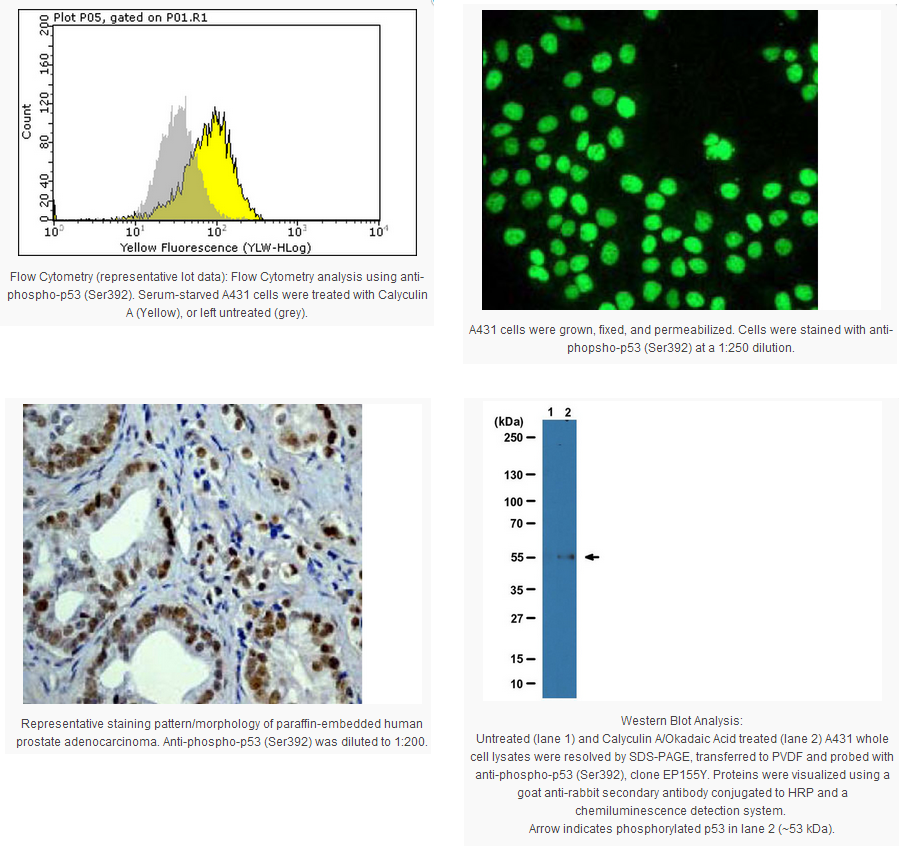
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
描述:
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R, H | WB, IH(P), ICC, IP | Rb | Unpurified | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Unpurified |
| Presentation | Unpurified rabbit monoclonal IgG in buffer containing 50 mM Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 0.15 M NaCl, 40% Glycerol, 0.01% sodium azide and 0.05% BSA. |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
原厂资料:
| Species Reactivity | Key Applications | Host | Format | Antibody Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R, H | WB, IH(P), ICC, IP | Rb | Unpurified | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Product Information | |
|---|---|
| Format | Unpurified |
| Presentation | Unpurified rabbit monoclonal IgG in buffer containing 50 mM Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 0.15 M NaCl, 40% Glycerol, 0.01% sodium azide and 0.05% BSA. |
| Packaging Information | |
|---|---|
| Material Size | 100 µL |
说明书
参考文献
本产品可用于的实验
京ICP备15036693号-2  京公网安备11010802025653 版权所有:北京逸优科技有限公司
0.13
京公网安备11010802025653 版权所有:北京逸优科技有限公司
0.13