描述:
Directions
Reconstitute the contents of one vial of lyophilised Nitrocefin SR0112 by adding the entire contents (2ml) of one vial of rehydration fluid SR0112A. This yields a working Nitrocefin solution of 500mg/ml, (approx 10-3 M) suitable for most applications.
Precautions
Nitrocefin, particularly in solution, is very light sensitive. The solution may be stored at -20°C for up to two weeks. INGESTION OR INHALATION, OR CONTACT WITH THE SKIN AND EYES SHOULD BE AVOIDED.
General Introduction and Intended Uses
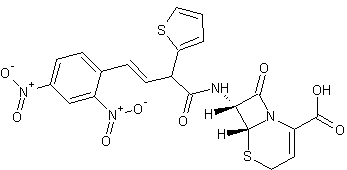
Nitrocefin is the chromogenic cephalosporin developed by Glaxo Research Limited (code 87/312; 3-(2,4 dinitrostyrl) - (6R,7R-7-(2-thienylacetamido)-ceph-3-em-4-carboxylic acid, E-isomer)1. This compound exhibits a rapid distinctive colour change from yellow (max at pH 7.0 = 390nm) to red (max at pH 7.0 = 486nm) as the amide bond in the beta-lactam ring is hydrolysed by a beta-lactamase (E.C 3.5.2.6); it is sensitive to hydrolysis by all known lactamases produced by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This characteristic reaction forms the basis of a number of methods suitable for diagnostic use.
Apart from its use in giving rapid indication of beta-lactamase potential, the reagent has been found extremely useful for the detection of beta-lactamase patterns from bacterial cell extracts on iso-electric focusing2,3,4 and has been used in inhibition studies in development work on beta-lactamase resistant antibiotics5.
Description of Use
Demonstration of beta-lactamase activity in bacterial cells.
Nitrocefin degradation should be used to give a rapid indication of beta-lactam inactivating systems and the result so obtained will, in most cases, predict the outcome of susceptibility tests with beta-lactam anti-microbials. However, it should not entirely replace conventional susceptibility testing as other factors also influence the results of such tests, and on occasion intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antimicrobials has not been correlated with production of beta-lactamase6. Nitrocefin degradation has been found to be highly efficient in detecting beta-lactamase producing isolates of Neisseriagonorrhoeae7,8, Haemophilus influenzae7,9,10,11 and staphylococci10,11.
Excellent results have also been obtained with certain anaerobic bacteria, notably with Bacteroidesspecies13,14,15. It should be emphasised that the efficacy of the Nitrocefin tests in predicting the beta-lactam susceptibilities of other micro- organisms is at present unproven. Another chromogenic cephalosporin, PADAC (Hoechst-Roussel) was not as effective as Nitrocefin in detecting staphylococcal beta-lactamase12.


 京公网安备11010802025653 版权所有:北京逸优科技有限公司
京公网安备11010802025653 版权所有:北京逸优科技有限公司